Truck drivers have a higher-than-average risk for diabetes, which affects over 30 million Americans. That’s largely because the sedentary nature of truck driving contributes to obesity and lack of physical activity, which increases the risk for Type 2 diabetes.
DIABETES TYPES
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form of diabetes, occurs when the body develops insulin resistance and is unable to use insulin properly. This causes an inability to regulate blood glucose levels properly, causing levels of blood glucose, or sugar, to rise too high.
Only about 5 percent of people who have diabetes have Type 1 diabetes, which is not as straightforward as Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes typically is diagnosed in children and young adults, according to the American Diabetes Association. It is considered to be caused by an immune reaction in which the body attacks itself. Family history and age are considered risk factors.
SYMPTOMS
Frequent thirst and excessive urination can be indicators of diabetes. Extreme fatigue is another potential indicator. Blurry vision, slow-healing sores or bruises and tingling or pain in the hands or feet are other common symptoms.
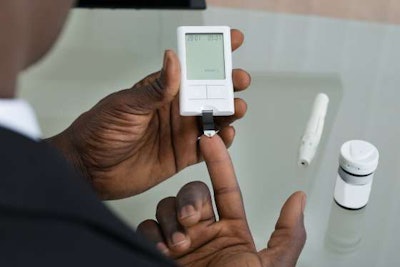 Diabetics must monitor their blood glucose levels.
Diabetics must monitor their blood glucose levels.RISK FACTORS
The Centers for Disease Control says Type 2 diabetes risk factors are being overweight, 45 years of age or older, physically active less than three times a week and having a family history of Type 2 diabetes. African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, American Indians and Alaska natives are at a higher risk for Type 2 diabetes.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
The main treatment for Type 1 diabetes is insulin, either by injections or through an insulin pump. Typically, patients check their glucose level five to seven times a day and give themselves insulin injections four to seven times a day, depending on glucose levels and frequency of eating. They also need to follow up with their endocrinologist every three months and work closely with their medical team.
Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with lifestyle changes: eating healthier, exercising regularly and losing weight if you’re overweight. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) advises overweight individuals to lose 5 to 7 percent of their weight and to exercise for at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week.
Your doctor can help you formulate a realistic exercise and diet plan. To get started, you can walk around your truck during downtime or bring weights on the road for other exercises. NIDDK recommends eating smaller portions and eating foods with less fat to cut calories. Drinking water instead of sweetened beverages will do the same.
Type 2 diabetes can be controlled with medication and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Mayo Clinic suggests seeing a doctor for blood glucose screening if you are 45 or older and overweight, or if you are younger than 45 and overweight with one or more of the additional risk factors for Type 2 diabetes.
GETTING A CDL EXEMPTION
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration requires interstate drivers with insulin-treated diabetes to obtain a medical exemption to maintain their commercial driver’s license. Those drivers can request an exemption from their certified medical examiner. To apply for an exemption, drivers will need to have an endocrinologist complete an evaluation and also have their vision evaluated.